Pulmonary Volumes
The fall in FRC reduces the volume of oxygen left in the lungs during apnoea. Combined with greater oxygen demands, this results in the more rapid fall of maternal PaO2 during apnoea.
The diagram shows the decrease in arterial PaO2 after 1 min of apnoea in pregnant and non-pregnant patients. (Archer & Marx, 1974.)
The faster fall in PaO2 during apnoea in pregnancy contributes to difficulties with general anaesthesia during pregnancy by reducing the time available for airway manipulation during induction.
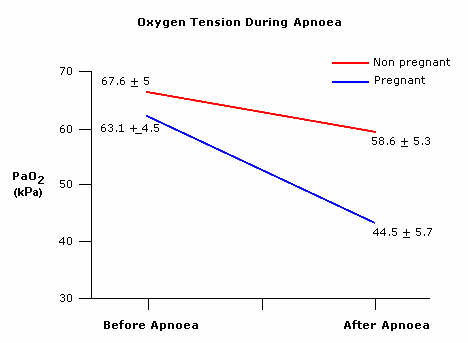
Fig 1 Decrease in arterial PaO2