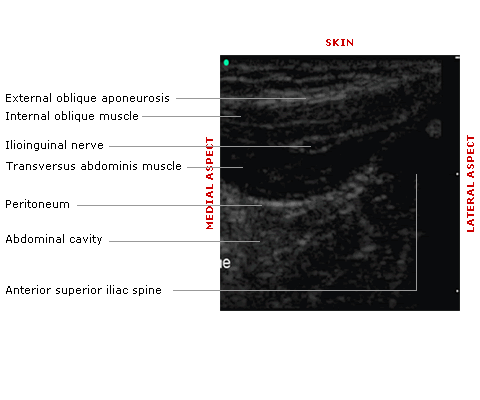
Sono-anatomy
US studies have shown that when a US probe is placed over the ASIS only half of patients have two muscle bellies (the external oblique muscle having become an aponeurosis) (Fig 1). The other half have three muscle bellies.
Importantly, no body demographic correlated nerve depth or position to ASIS or peritoneum.
According to US studies the average distance of the nerves to the peritoneum is 3.3 mm with the shortest distance described being 1 mm (Table 1).
Therefore, intraperitoneal injection is probably more common than originally thought. Although complications are rare, you should still seek to avoid this happening.
|
Weight (kg) (no. of patients) |
ASIS–ilioinguinal nerve (mm) |
Skin–ilioinguinal nerve (mm) |
Skin–iliohypogastric nerve (mm) |
Ilioinguinal nerve–peritoneum (mm) |
|
5 (8) |
5-10.3 |
5-9 |
3.9-7.8 |
1-4 |
|
13 (5) |
6.3-13 |
4.8-8.9 |
5.4-8.9 |
1.7-4 |
|
16 (4) |
11.3-13 |
5.4-12 |
5.5-11 |
3-4.6 |
Table 1 The range of distances measured from the ASIS and the skin to the iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves and from the ilioinguinal nerve to the peritoneum in children of three different weights, taken from Willschke H. et al. (2005)