Breathing
The recovery team need to know the patient’s breathing issues pre- and peri-operatively. The patient may have severe COPD and need to sit upright. He or she may have been hypoxic during the operation necessitating high FiO2.
Describe intra-operative ventilatory requirements. For example, spontaneous ventilation or mechanical ventilation. Mention any intra-operative problems with ventilation. For example, an inability to maintain adequate saturation, bronchospasm or laryngospasm.
Question: Why is patient posture and supplemental oxygen important in recovery and on the ward?
Click here for the answer.
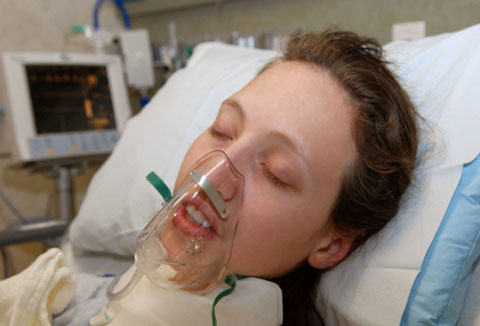
The recovery team need to know the patient’s breathing issues pre- and peri-operatively. The patient may have severe COPD and need to sit upright. He or she may have been hypoxic during the operation necessitating high FiO2.
Describe intra-operative ventilatory requirements. For example, spontaneous ventilation or mechanical ventilation. Mention any intra-operative problems with ventilation. For example, an inability to maintain adequate saturation, bronchospasm or laryngospasm.
Question: Why is patient posture and supplemental oxygen important in recovery and on the ward?
Answer: Respiratory performance is improved when sitting compared with the supine position. If the patient is drowsy, has underlying chest disease, is receiving morphine via patient controlled analgesia (PCA) or an epidural, supplemental oxygen should be provided.
