When an individual is awake, the gag reflex is initiated if an unfamiliar object is placed in the mouth and it touches the palate, tonsil, posterior part of the tongue or the posterior pharyngeal wall. The afferent side of the reflex is glossopharyngeal, the efferent side is vagal.
The gag reflex will be stimulated by insertion of an oral airway (or LMA) in a patient who is awake or lightly anaesthetized.
A nasopharyngeal airway is much better tolerated in a patient who is awake as it does not stimulate the gag reflex, provided the airway does not extend beyond the tip of the soft palate (Fig 1).
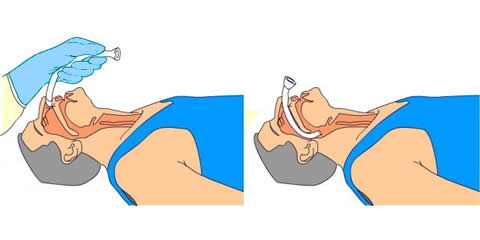
Fig 1 Nasopharyngeal insertion