Tonsils
The palatine tonsils, more commonly simply referred to as the tonsils, are collections of lymphoid tissue between the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches, the 'pillars of the fauces'.
Like the adenoids, the tonsils also hypertrophy during childhood. Tonsillectomy is indicated for frequent infection or obstructive sleep apnoea. Large tonsils may cause airway obstruction after induction of anaesthesia.
The sensory nerve supply to the tonsil is from branches of three nerves, i.e. the glossopharyngeal, maxillary and mandibular nerves. Infiltration analgesia into the tonsillar bed is more effective than attempting nerve blockade.
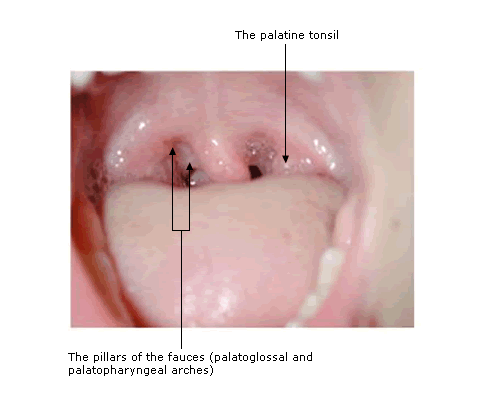
The Palatine tonsils