Pericardial Effusion
Fluid may collect in the pericardial sac. This is known as a pericardial effusion. A large collection causes cardiac tamponade.
Pericardial collections may be secondary to:
- Cardiac surgery
- Trauma
- Inflammation of the pericardium, e.g. viral pericarditis, uraemia
Question: What are the physiological consequences of a pericardial effusion?
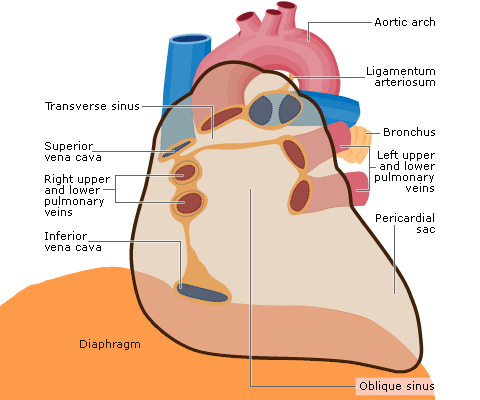
Fluid may collect in the pericardial sac. This is known as a pericardial effusion. A large collection causes cardiac tamponade.
Pericardial collections may be secondary to:
- Cardiac surgery
- Trauma
- Inflammation of the pericardium, e.g. viral pericarditis, uraemia
Question: What are the physiological consequences of a pericardial effusion?
Answer: The size of the pericardial sac is limited by the fibrous pericardium. As the volume of the effusion increases the heart becomes compressed and, in particular, cardiac filling becomes impaired, resulting in low cardiac output.
Cardiac tamponade is a potentially reversible cause of cardiac arrest.
