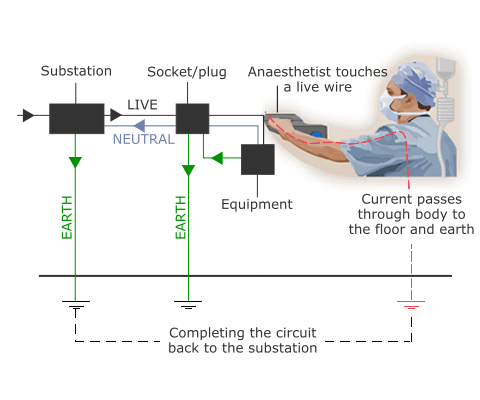
If a person were to touch a live wire in theatre, an electric current would pass through the body to the floor and earth, thus completing a circuit back to the sub-station (Fig 1). The effect of the subsequent shock depends on the magnitude of the current.
Electrical current is measured in amperes (A). Current (I) in a circuit depends on the electrical barrier presented to the voltage (V) applied. For Direct Current, resistance (R, in Ohms) is the term used for this barrier and enables the current to be calculated according to Ohm's Law:
Voltage = Current × Resistance (V = IR).
For alternating current, the term impedance (Z) is used instead of resistance, and can be similarly used in Ohm's Law to calculate current. Impedance varies with frequency.
As the resistance or impedance falls, current
increases
(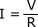 or
or 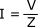 )
)